SEO has evolved over the years.
Thankfully, Google has managed to rid us of spammy practices like content farming and keyword stuffing and left us with a powerful marketing tool that thrives on easy-to-read, helpful, and comprehensive content.
However, SEO is not a quick-win strategy: it requires a long-term investment, and as long as brands are persistent, it delivers value.
So how do you harness the power of SEO for your brand?
In this beginner’s guide to SEO, you’ll discover:
- What is SEO?
- What are the benefits of SEO?
- What are the challenges of SEO?
- 3 examples of successful SEO campaigns
- How to implement a winning SEO strategy for your brand
Let’s get started.
What is SEO?
SEO stands for “search engine optimization” and refers to the process of making your site better for search engines.
The practice of SEO involves continuously optimizing your website for higher rankings and brand exposure in the organic (non-paid) search results so that you increase both the quality and quantity of your website traffic.
SEO activities include running technical audits, targeting high-intent keywords, creating quality content, and building backlinks.
SEO vs SEM
The terms SEO and SEM are often used interchangeably, but there is a subtle difference.
SEM stands for “search engine marketing” and refers to all the activities you perform to earn placement in the non-organic (paid) search engine results.
SEM activities include targeting high-value keywords, optimizing ad copy, display creatives and landing pages, and monitoring key metrics.
Audio SEO
The pandemic has accelerated the development of synchronous audio content (like Clubhouse, now valued at $4 billion) and asynchronous audio content ( 900K podcasts created in 2020 – 3X more than in 2019).
But standard SEO techniques (based on over 200 factors used by Google) are of no value to podcasters unless they repurpose the material as written content.
Google recently launched its Google Podcasts app (400K downloads/month) and knows it requires other methods to classify and prioritize audio content.
Enter Audio SEO – a new industry that may soon become a sub-branch of traditional SEO and that already weighs in at $80 billion. For example:
- Build tools to enrich audio content, such as Entale (£2.4M raised in the UK) or Adori Labs ($355k raised in the US), which allow creators to include links, images, videos, and promo codes inside a podcast.
- Become a specialist in Audio SEO
- Create tools to measure the performance of audio content and identify promising niches.
Source: Sounder
SEO Glossary
- SEO stands for “search engine optimization” and refers to the process of making your site better for search engines.
- SEM stands for “search engine marketing” and refers to all the activities you perform to earn placement in the non-organic (paid) search engine results.
- SEP stands for Search Engine Promotion and includes the efforts to generate backlinks from other websites, sometimes referred to as offsite SEO.
- User Intent, also called Search Intent, is the main goal behind a user’s Google search.
- SERP(s) stands for Search Engine Results Page(s) and are Google’s response to a user’s search query. SERPs tend to include organic search results, paid Google Ads results, Featured Snippets, Knowledge Graphs, and Video Carousels.
- Technical SEO is the process of ensuring that a website meets the technical requirements of modern search engines with the goal of improved organic rankings. Important elements of Technical SEO include crawling, indexing, and website architecture and speed.
- On-page SEO (also known as “on-site SEO”) is the practice of optimizing web page content for search engines and users. Common on-page SEO activities include optimizing title tags, content, internal links, and URLs.
- Off-page SEO (also called “off-site SEO”) refers to actions taken outside of your website to increase the site’s search engine rankings. Common off-page SEO actions include building backlinks, encouraging branded searches, and increasing engagement and shares on social media.
What are the Benefits of SEO for Your Brand?
Let’s examine the advantages of using SEO for your brand:
- Improves traffic – SEO increases both the quality and quantity of your website traffic by providing valuable and helpful content to searchers. Ranking at or near the top helps you target the right audience, who are more likely to use your services or purchase your products.
- Extends web presence – SEO can also help you rank in other web properties like Google Maps, Google My Business, and other review sites like Yelp and Trusted Advisor.
- No PPC costs – With SEO, you don’t need to pay for ads. Over time you can attract traffic to your site without having to pay for clicks.
- SEO gets more clicks than PPC – Although PPC ads appear above organic rankings, 71% of searches result in a click on an organic result on the first page.
- SEO helps PR – Although SEO and PR may seem like entirely separate marketing strategies, you can use them together to maximize the results you see from each.
- More discoverable – 61% of marketers say improving search engine optimization (SEO) to grow their organic presence online and become more discoverable is their top inbound marketing
- Better user experience – Good SEO practice helps design your website so that your visitors have an easier time navigating and finding the information they want and, in turn, convert visitors into customers.
- You’re an authority – The better the content, the more people recognize you as an authority in your niche, trust your opinion, and most likely buy from you.
- SEO is relatively cheap – SEO costs money, but it’s relatively inexpensive compared to traditional marketing. And, better still, it’s a sound business investment for years to come.
What are the Challenges of SEO for Your Brand?
Of course, there are always pros and cons, so let’s examine the disadvantages of SEO for your brand.
- Competition – If your SEO strategy is working and you’re ranking high in the search results, then you can be sure that your competitors will be monitoring your site to see what they learn and steal from you.
- Algorithms– Google’s search engine is continually being updated with minor and major algorithmic changes. You need to be aware of these updates and adjust your strategy accordingly.
- Penalties – Some algorithmic updates could lead to you losing rankings or getting Google penalties.
- Time – SEO isn’t a fast-moving process. Even if you follow best practices, you need patience for SEO to take effect and rank your content near the top of search engine results pages.
- No guarantee – There’s no guarantee that SEO will lead to more traffic and revenue.
- Budget – SEO requires time and investment for tools and resources, whether you use in-house resources or outsource to an agency.
- Paid search – There’s always the possibility that competitors can outrank your organic position with a paid search result.
- Decreasing >CTRs – As Google is crowding out the organic search results with SERP Features, like Answer Boxes, People Also Ask, Video Carousels, and more, it’s harder to get clicks to your website.
3 Examples of Successful SEO Campaigns
Let’s take a look at three examples of successful SEO campaigns.
Example #1: SPOTIO’s SEO roadmap for immediate, short, and long term growth
SPOTIO (a leader in the field sales software niche) approached Virayo (a digital marketing agency) to help it launch a new website and reposition itself as a leader in the B2B field sales market.
Virayo devised an immediate, short, and long term action plan:
- Immediate: Migrate to a new website design and information architecture without losing organic traffic.
- Short-term: Maintain market share in door-to-door sales software niche while breaking into new B2B field sales market.
- Long-term: Build SEO strategy to drive more organic traffic and leads.
The initial results were spectacular:
- 50% increase in organic traffic within 30 days of site migration.
- Increased volume of higher value B2B leads and sales.
- Top 3 keyword rankings across both field sales and door-to-door markets.
Since then, SPOTIO has continued to improve its position as a market leader with more organic traffic and leads.
Example #2: America’s Best Contacts & Eyeglasses’ Two-pronged SEO approach brings vision to life and increases traffic more than 40%
America’s Best Contacts and Eyeglasses is a national eye care brand with more than 500 retail stores. They engaged Cardinal Digital Marketing to help them improve their online presence and authority.
Cardinal developed a two-pronged SEO approach:
- Onsite: Develop a comprehensive keyword strategy and identify the most profitable keywords to restructure their web presence, update all metatags, and enhance their web page content.
- Offsite: Update and optimize online directories and develop a robust link-building campaign to increase their authority within the industry, as well as improve their page rank.
The new SEO strategy delivered impressive results. Americas Best ranked on the first page for 120 of their targeted keywords. And, as a result, they saw a 40.9% increase in website traffic and a 31.5% increase in pageviews.
Example #3: How Brian Dean increased organic traffic on his site 652% in 7 days
The final example shows how SEO expert Brian Dean increased organic traffic on his site, Backlinko, using a technique he calls “Skyscraper Technique 2.0”. (It’s an update on his original Skyscraper Technique).
Brian noticed that one of his earlier articles – The Complete SEO Checklist – had dropped in search engine rankings onto page 2 of the results. As he puts it: “My content was a smash hit… then it flopped.”
When he analyzed his content, he found one crucial ingredient was missing: User Intent.
There are three key components to his Skyscraper Technique 2.0:
- Step #1: Figure out user intent – Use Google to understand what kind of information searchers are looking for: informational, navigational, commercial, or transactional.
- Step #2: Satisfy user intent – Make sure your content fulfills that intent. You can apply this to brand new posts you are planning or by improving an existing piece of content.
- Step #3: Optimize for UX signals – Optimize dwell time, organic CTR, and bounce rate. For example, you could use videos, a table of contents, short intros, detailed illustrations, and proper headings.
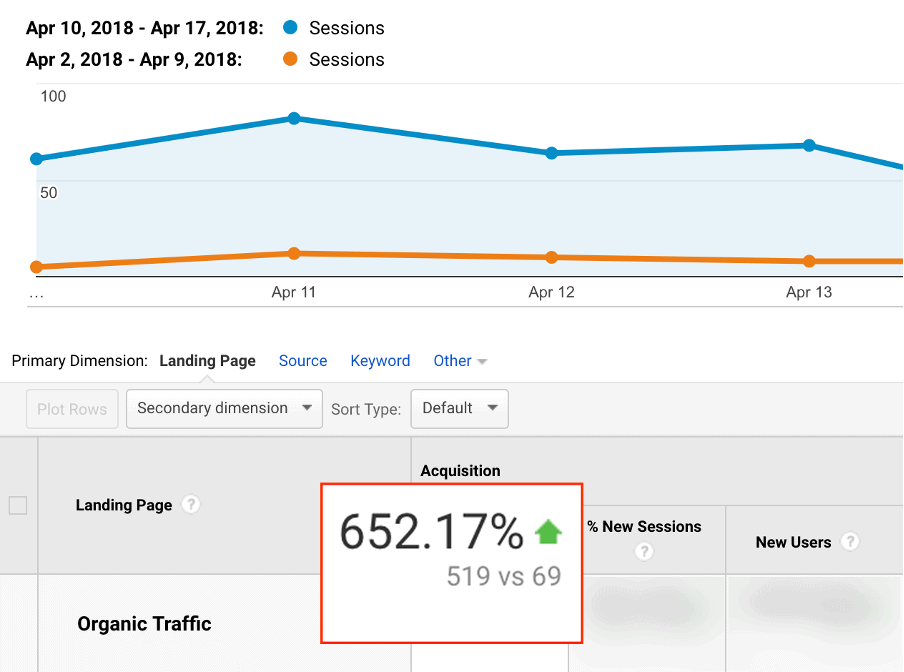
After optimizing user intent, organic traffic rocketed, and the page went from ranking in position #11 to #5. And at the time of writing, it ranks in second spot:
Feeling inspired by these examples? Now it’s your turn.
How to Implement a Winning SEO Strategy for Your Brand
A robust SEO strategy helps you identify the bigger picture by answering these questions:
- Where are you now?
- Where do you need to get to?
- How are you going to get there?
You’ll also need to consider your budget, resources, and timeframe in your planning.
Follow our 7-step guide to implementing your SEO strategy:
- Set your goals
- Plan your content
- Produce your content
- Optimize your content (On-page SEO)
- Optimize your site (Technical SEO)
- Promote your content (Off-page SEO)
- Measure your performance
Let’s begin.
#1. Set your goals
Benchmark your current performance
The first thing to do is to benchmark your current performance. You can’t set goals and measure success unless you know how your site’s performing right now.
As a baseline, you need to be benchmarking your site traffic and keyword rankings.
Analyze your competitors’ performance
At this stage, you should also check the SERPs to analyze your competitors’ performance and strategies and identify where they’re ahead of you:
- Check which pages drive the most organic traffic to their site.
- Identify the keywords your competitors are ranking for, but you are not.
- Check where your competitors’ backlinks are coming from.
Set your goals and KPIs
With those background tasks completed, you can set your goals and KPIs.
- Goals are the end outcome that you want to achieve.
- KPIs are the metrics that indicate progress towards your goals.
For example:
- Goal = increase organic revenue by $500,000 over the next 12 months.
- KPIs = the metrics to track are increases in organic impressions, organic traffic, and keyword rankings.
#2. Plan your content
Keywords are central to search engine optimization, so keyword research is usually the first step of an SEO strategy. However, there are now two strands to keyword research:
- Pillar pages are usually broad and link to multiple topic cluster pages. They act as a hub for a specific topic.
- Topic clusters are more in-depth pages that answer a specific question about your broad topic and link back to the pillar page.
For example, if “SEO” were our pillar page (broad topic), it would have cluster topics like Technical SEO, Local SEO, On-page SEO, and Off-Page SEO:
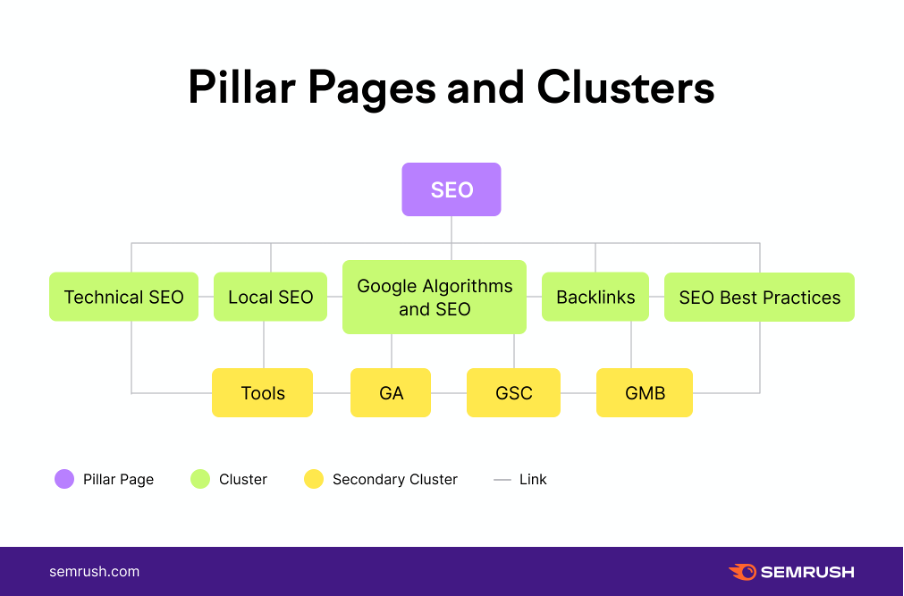
Topic clusters help you establish topical relevance for sections of your site so that it’s clear to visitors and Google what your content is about.
Make a list of topics for your pillar pages
The first step is to create a list of keywords for your pillar pages. These keywords define topics broadly, such as “Paleo diet”, “running shoes”, or “CRM software”. They are usually one or two words long and are sometimes called “head” or “short-tail keywords”.
Aim to create a list of 5-10 short-tail keywords that are relevant to your business and being searched for by your target audience.
Make a list of long-tail keywords based on these topics
Once you have a list of topics, you can create a list of 5-10 long-tail keywords for each topic.
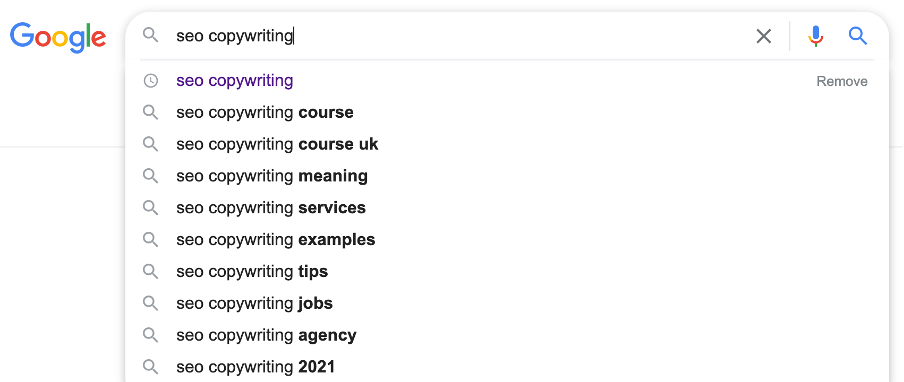
You can easily find longer keywords that customers search for using Google Suggest.
Enter a keyword into Google’s search field, and it will auto-populate a list of suggestions:
You can also find longer keyword ideas in the “People Also Ask” boxes:
And the “Related Searches” at the bottom of the page:
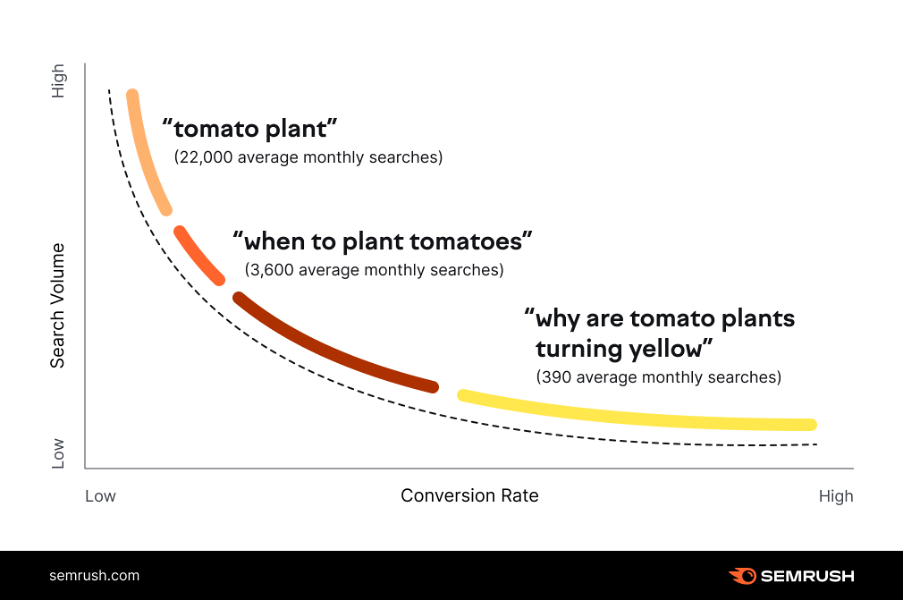
Longer keywords (known as “long-tail keywords”) tend to be less competitive than “short-tail” terms:
You can use your SEO tool of choice to check out the search volume and competition levels for your keywords.
So at the end of this planning phase, you should have a list of 5-10 pillar pages, each with 5-10 cluster topics.
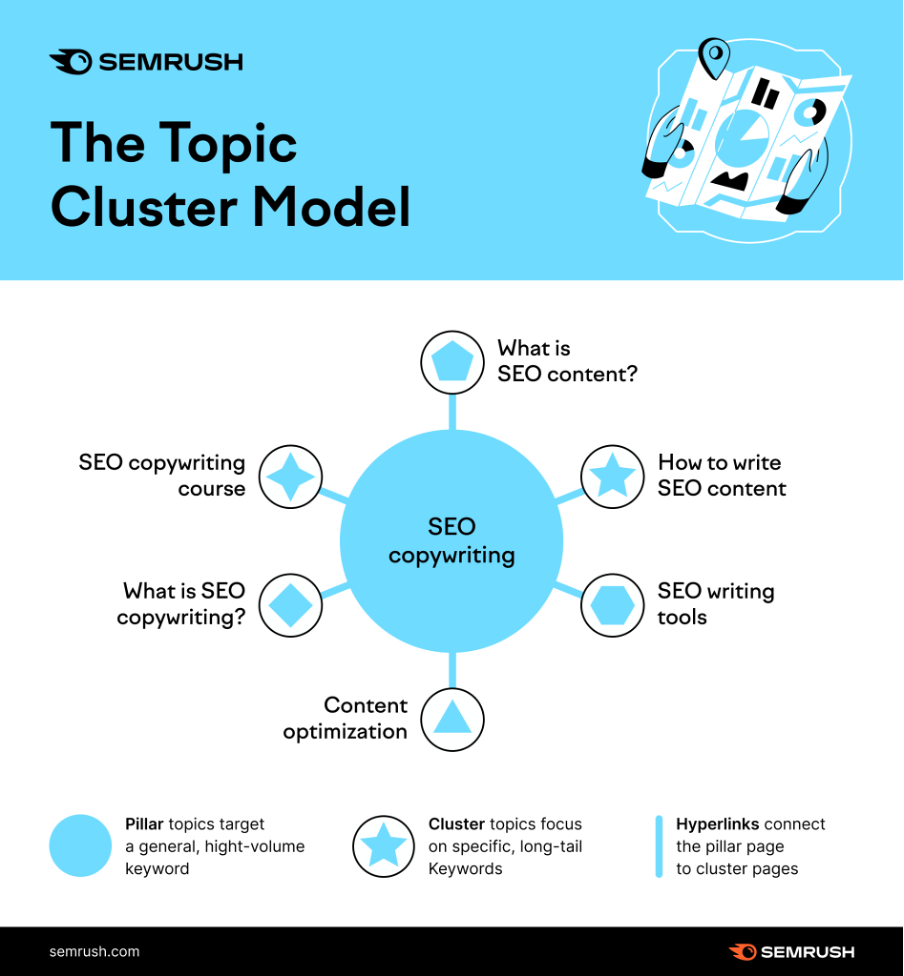
For example, if one of your pillar pages was “SEO Copywriting”, your cluster topics might be:
- What is SEO content?
- How to write SEO content?
- SEO writing tools
- Content optimization
- What is SEO copywriting
- SEO copywriting course
And would look something like this:
#3. Produce your content
Now that you’ve planned your pillar pages and topic clusters, it’s time to create your content. Again, there’s a two-pronged approach to follow when you produce each piece of content:
- Analyze the existing content
- Create something better
Analyze the existing content
First, you want to check what’s already working for your keywords, so enter one of your keywords into Google and check the first page results.
For example, if you enter “SEO writing tools”, you can see that most of the results (eight out of 10) are lists of tools:
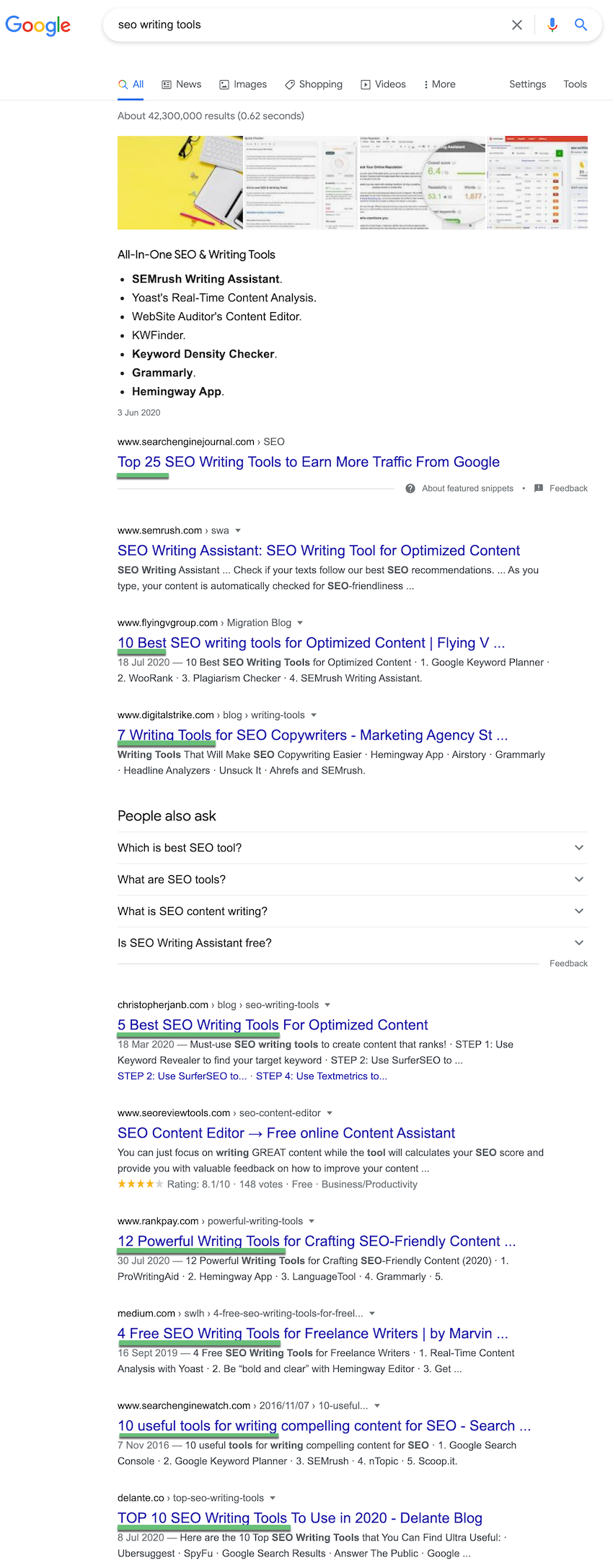
So if you wanted to cover that topic, you’d need to create a “list post” on your blog to match the existing SERP.
Create something better
If you want to rank higher than the existing content, then you need to create something better. For example, the list posts above cover 5-25 tools, so you might want to create a list of 50 SEO writing tools. But it’s not just quantity that needs to be better – you need to focus on creating better quality.
Remember the example from Backlinko where he needed to match and satisfy user intent and create something better with images, videos, and layout?
That’s what we’ll cover in the next step when we optimize your content.
#4. Optimize your content (On-page SEO)
On-page SEO covers many factors for optimizing each page on your website. The idea is to provide a positive user experience for your visitors and help search engines understand your content.
In this guide, we’ll cover three factors:
- Keywords
- Content
- Images
Keyword optimization
When you create your content, whether it’s a pillar page or a topic cluster, there are a few strategic places where you need to include your target keyword:
- URL
- Page title
- Meta description
- Main heading (H1)
- Opening sentence/paragraph of the page
- Page subheadings (H2/H3 etc.)
For example, if you check our blog post on Local Marketing, you can see some of these factors in play:
- URL = https://www.loomly.com/blog/local-marketing/
- Page title = Local Marketing: How to Reach Customers in Your Area
- Meta description = Local marketing is a strategy that targets potential customers within a specific radius – typically 50 miles – of the physical location of a business.
- Main heading (H1) = same as the page title
- Opening sentence of the page = Local marketing is becoming more important than ever, especially with local stores needing to move online due to the pandemic.
- Page subheadings (H2/H3 etc.) =
- <H2> What is Local Marketing?
- <H3> Local Marketing vs Global Marketing
- <H2> Why is Local Marketing More Important Than Ever?
- <H2> 3 Examples of Successful Local Marketing Campaigns
- <H3> Nike
- <H3> Airbnb
- <H3> Brent Jones
- <H2> How to Promote Your Business With Local Marketing
- <H3> Local SEO
- <H3> Content Marketing
- <H3> Paid Advertising (Search and Social)
- <H3> Further local marketing strategies
- <H2> Local Marketing in a Nutshell
- <H2> What is Local Marketing?
Pro Tip: Use Short, Keyword-Rich URLs. Research by Backlinko found that when it comes to SEO, short URLs tend to outrank long URLs:
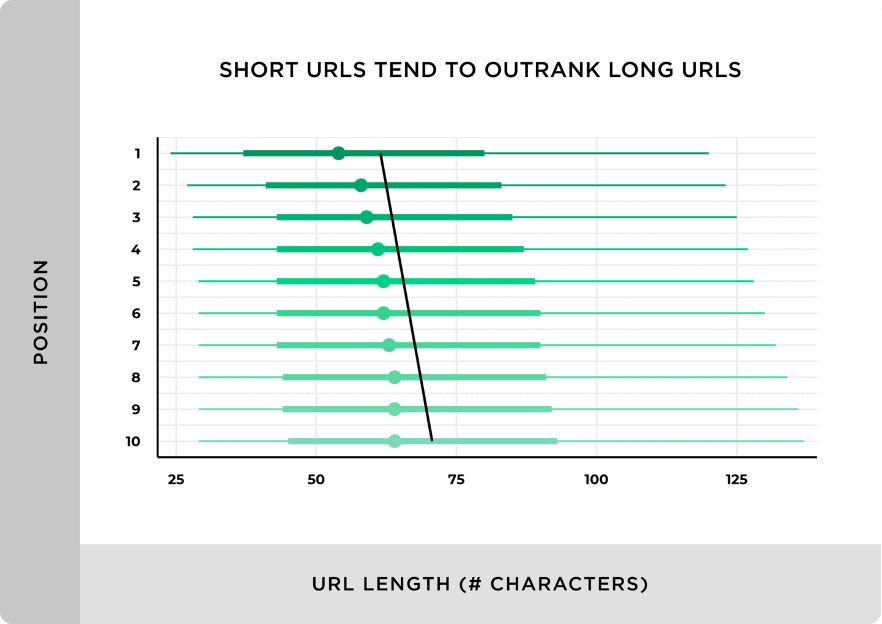
Plus, they’re more user-friendly!
Content optimization
We already highlighted that you need to map your content type to the existing SERPs. But here are three more factors to optimize.
a) Content length
There’s no definitive answer as to how long your content should be. You can check what’s already ranking for your target keyword and use that word count as an indicator.
The Backlinko-Ahrefs search engine ranking study couldn’t find a direct relationship between word count and rankings, even though the average word count was evenly distributed among the top 10 results.
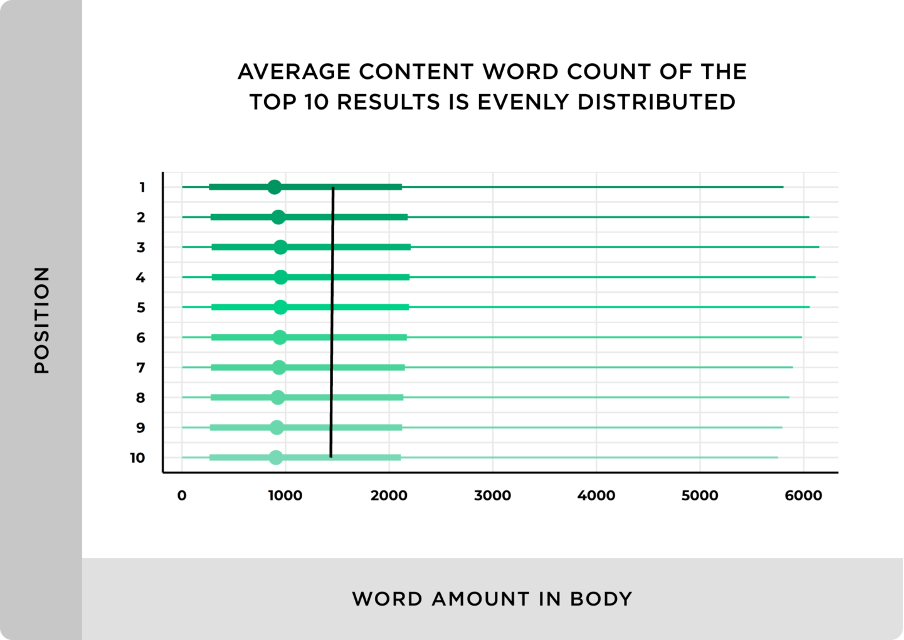
Takeaway: The average Google first page result contains 1,447 words, but you’ll need to check each target keyword for a true reflection.
b) Content quality
Two of Google’s algorithms reveal what type of content it favors:
- Hummingbird wants in-depth, comprehensive, and authoritative content.
- RankBrain wants easy-to-read, helpful, and comprehensive content.
When the Backlinko-Ahrefs search engine ranking study ran a subset of their dataset through the content analysis tool Clearscope, they found a clear correlation between “Content Grade” and Google rankings in both desktop and mobile results:
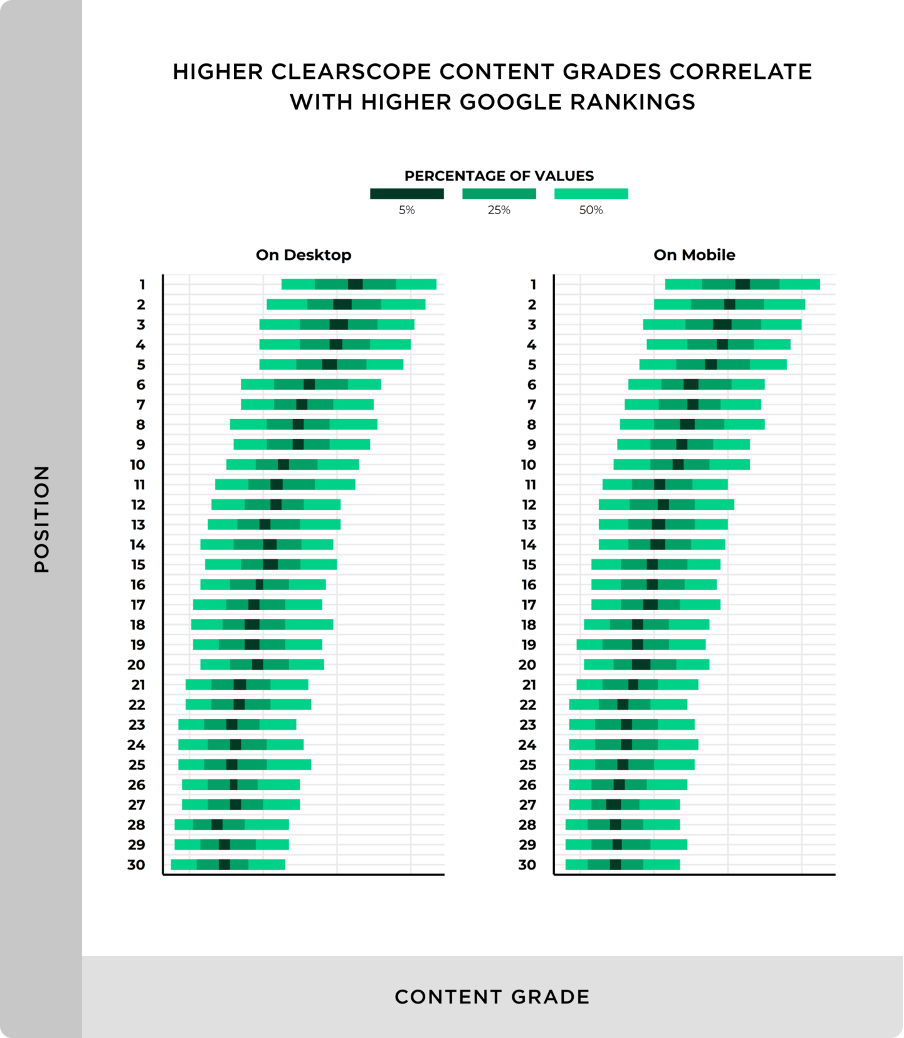
Takeaway: Comprehensive content with a high “Content Grade” significantly outperformed content that didn’t cover a topic in-depth.
c) Content layout
Again, if you check our article on Local Marketing (or any other article), you can see all these actions in play:
- Craft a winning headline
- Start with a short intro
- Use subheadings
- Write in short paragraphs
- Use bullet points
- Add visuals
- Link to relevant internal and external resources
Image optimization
There are several steps you can take to optimize your images for search engines and improve the user experience on your website. Plus, you can rank higher in Google Image Search – the specific search engine for images.
- Resize your images for the web – ensure your images are sized to fit your webpage rather than using the default size.
- Reduce the file size – use tools like ShortPixel, TinyPNG, or Kraken to compress images by 65% without losing the quality.
- Name your files appropriately – give your images a descriptive filename that provides context. Also, separate the words with dashes (stunning-sunset.jpg), not underscores (stunning_sunset.jpg).
- Add some Alt Text – always add a meaningful description to the Alt Text on your images to help visually impaired readers understand what they relate to.
- Add a descriptive title and caption – Google extracts information about the subject matter of the image from the page’s content, including image captions and titles.
#5. Optimize your site (Technical SEO)
While On-Page SEO covers how to optimize individual pages, Technical SEO covers how to optimize site-wide factors.
If your site has technical SEO issues, they could hinder its performance and prevent it from ranking as well as it could if they were fixed.
Think of Technical SEO as improving the technical foundation of your whole website so that individual pages run smoothly and rank higher.
The best way to check for technical issues is by running a Site Audit from your preferred SEO tool.
For example, the SEMrush Site Audit Tool can analyze your site against more than 130 technical SEO problems, such as duplicate and thin content, broken links, HTTPS implementation, crawlability, and indexation problems. These are categorized by errors, warnings, and notices based upon their severity and ability to impact performance:
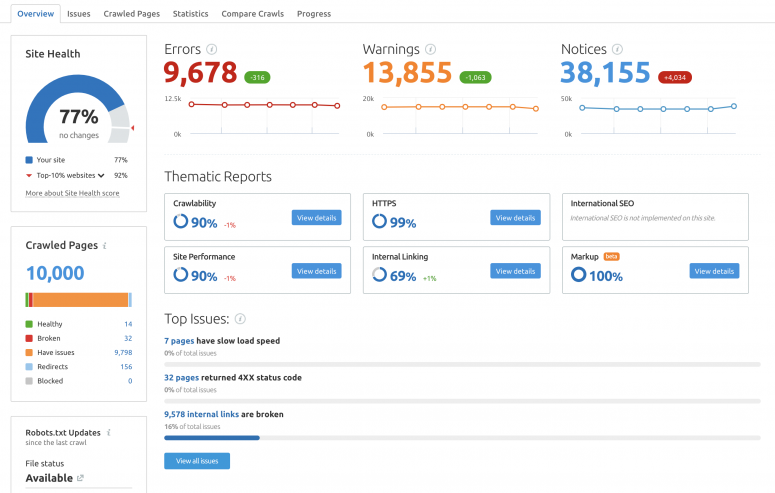
You can run the audit every month to ensure everything is in tip-top condition.
#6. Promote your content (Off-page SEO)
After you’ve completed your On-Page and Technical SEO tasks, it’s time to turn your attention to Off-page SEO, sometimes referred to as search engine promotion (SEP).
Off-page SEO refers to anything done outside of your website with the potential to increase search engine rankings.
Link-related off-page factors
Backlinks remain one of Google’s top three ranking factors, so you need a solid link-building strategy.
You can use various techniques and strategies to attract backlinks to your content, including:
Non-link-related off-page factors
Aside from building backlinks, there are other off-page factors, including:
- Brand mentions
- Social signals
- Google My Business
- NAP citations
- Reviews
The latter three are all covered in our Local Marketing guide.
#7. Measure your performance
After you’ve created your strategy and started to implement it, you’ll need to measure your performance.
Like all marketing strategies, you’ll need to continually track your SEO goals and metrics, assess your progress, identify possible areas for improvement, and adjust accordingly.
Improving and updating content by removing outdated screenshots and images and replacing them with fresh ideas can return tremendous results. For example, Brian Dean boosted organic traffic to one article by 260.7% using his Content Relaunch process.
Whether it’s creating new content, optimizing existing content, acquiring more backlinks, or ensuring that no technical issues appear, you need to continually evaluate and refine your SEO activities to ensure you’re successful.
SEO in a Nutshell
SEO stands for “search engine optimization” and refers to the process of improving your site for search engines. SEO activities include running technical audits, targeting high-intent keywords, creating quality content, and building backlinks.
Follow our 7-step guide to implement your SEO strategy:
- Set your goals
- Plan your content
- Produce your content
- Optimize your content (On-page SEO)
- Optimize your site (Technical SEO)
- Promote your content (Off-page SEO)
- Measure your performance